Introduction
Cause and effect relationships are fundamental aspects of understanding the interconnectedness of events and phenomena in our world. By exploring these relationships, we gain insight into how one action or event can lead to another, thereby shaping outcomes and influencing outcomes. In this exploration, we explore five distinct types of cause and effect relationships, each offering unique perspectives and implications. From direct causation to complex chains of events, understanding these relationships empowers us to analyze situations more critically, anticipate consequences, and make informed decisions. Embark with us on an exciting journey of unraveling the intricacies of cause and effect, and gain invaluable insights along the way
Definition of Cause and Effect
Cause and effect is a fundamental principle that describes the relationship between events, where one event (the cause) brings about another event (the effect). In essence, it asserts that every action or occurrence has consequences, leading to subsequent outcomes. The cause is the factor or event that initiates or triggers a sequence of events, while the effect is the result or consequence of that initial action.
Understanding cause and effect allows us to comprehend the interconnectedness of phenomena, identify patterns, predict outcomes, and make informed decisions based on the understanding of how actions lead to specific results. This concept is pervasive across various disciplines, including science, philosophy, sociology, and literature, providing a framework for analyzing and interpreting phenomena in our daily lives and in the world at large.
Examples of Cause and Effect in Sentences
- Heavy rain led to flooding in the city, causing streets to be submerged, traffic disruptions, and property damage.
- Lack of exercise results in poor physical health, contributing to obesity, heart disease, and other health issues.
- Increased greenhouse gas emissions contribute to global warming, leading to climate change with melting ice caps, rising sea levels, and extreme weather patterns.
- Studying diligently results in better grades in school.
- Exposure to secondhand smoke increases the risk of respiratory problems like asthma, bronchitis, or other respiratory conditions.
- Regular savings contribute to financial security in the long term.
- Poor communication leads to misunderstandings in relationships causing conflicts and misinterpretations.
- Overuse of antibiotics leads to antibiotic resistance, making infections harder to treat and posing a serious public health threat.
- High levels of stress contribute to mental health issues such as anxiety and depression, negatively impacting emotional well-being with symptoms like insomnia, irritability, and difficulty concentrating.
- Investing in education leads to higher earning potential for individuals with advanced degrees or specialized skills.
5 Types of Cause and Effect Relationships
Understanding cause and effect relationships is crucial in various fields, from science and history to personal development. Here are five common types:
1. Direct Cause and Effect: This is the most straightforward type, where one event directly leads to another. For example, dropping a ball (cause) results in it falling to the ground (effect). The cause and effect are closely linked in time and space, and there’s minimal ambiguity.
2. Indirect Cause and Effect: Here, there are intermediary steps between the cause and effect, making the connection less obvious. For example, studying hard (cause) might lead to good grades (effect) only through the intermediate steps of improved understanding and exam performance. This type allows for complex chains of events, where initial actions have delayed or indirect consequences.
3. Multiple Causes, Single Effect: In this case, several independent factors contribute to a single outcome. For example, getting sick (effect) could be caused by a combination of stress, lack of sleep, and exposure to an illness. Identifying all contributing factors is crucial for understanding the full picture.
4. Single Cause, Multiple Effects: Here, a single event triggers multiple consequences. For example, an earthquake (cause) might lead to building damage, injuries, and power outages (effects). Analyzing these diverse outcomes helps assess the overall impact of the initial event.
5. Reciprocal Cause and Effect: This type involves a loop where two factors influence each other, making it challenging to determine which started first. For example, poverty (cause) might limit access to education, which (effect) perpetuates poverty, creating a cycle. Identifying these loops is crucial for breaking negative patterns and implementing effective solutions.
Cause and Effect Relationship Examples
Science:
In the of science, cause and effect relationships are crucial for understanding natural phenomena and the functioning of the universe. One example lies in the relationship between high levels of carbon dioxide emissions and global warming. When carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases are released into the atmosphere through human activities such as burning fossil fuels and deforestation, they trap heat from the sun, leading to a rise in global temperatures. This phenomenon, known as global warming, has far-reaching effects on the environment, including the melting of ice caps, rising sea levels, and disruptions to ecosystems and weather patterns.
Economics:
In economics, cause and effect relationships play a pivotal role in analyzing market dynamics and policymaking. For instance, an increase in interest rates by the central bank can have significant effects on the economy. When interest rates rise, borrowing becomes more expensive, leading to a decrease in consumer spending and investment. This slowdown in economic activity can ultimately result in lower levels of production, employment, and economic growth.
Health:
Understanding cause and effect relationships is essential in healthcare for identifying risk factors, preventing diseases, and promoting well-being. Smoking cigarettes, for example, is a well-established cause of numerous health problems. The chemicals in tobacco smoke damage the lungs and cardiovascular system, increasing the risk of lung cancer, heart disease, stroke, and respiratory conditions such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Recognizing the causal link between smoking and these health outcomes informs public health efforts to reduce tobacco use and improve population health.
Environment:
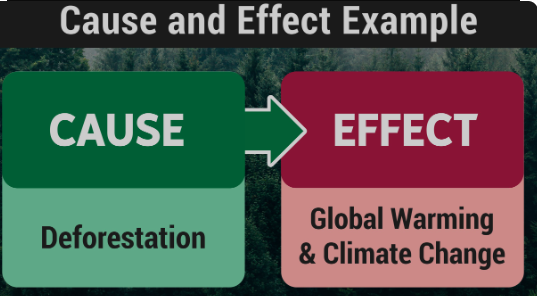
Environmental science relies on understanding cause and effect relationships to address pressing issues such as climate change, habitat loss, and pollution. Deforestation, for instance, is a significant cause of biodiversity loss and ecosystem degradation. When forests are cleared for agriculture, urbanization, or logging, habitats are destroyed, leading to the displacement and extinction of plant and animal species. This disruption of ecosystems can have cascading effects on ecosystem services, including water purification, carbon sequestration, and climate regulation.

Education:
In the field of education, cause and effect relationships help educators and policymakers understand the factors influencing academic achievement and student success. The quality of teaching and resources in schools, for example, can significantly impact student outcomes. Schools with well-trained teachers, adequate funding, and access to educational materials tend to have higher levels of student engagement, academic performance, and graduation rates. Recognizing the causal link between educational inputs and outcomes informs efforts to improve school quality and equity in education.
Technology:
Technological advancements often lead to cause and effect relationships that shape society and the environment. The development of renewable energy technologies, for instance, has the potential to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and mitigate climate change. By harnessing energy from sources such as solar, wind, and hydroelectric power, societies can decrease greenhouse gas emissions and transition towards a more sustainable energy future. This shift has ripple effects across various sectors, including energy, transportation, and manufacturing, influencing economic development and environmental conservation efforts.
Cause and Effect Essays
Completing a cause and effect essay effectively entails meticulous planning and organization. Start by revisiting your thesis statement to ensure clarity and accuracy, then organize your essay logically, outlining causes and effects with smooth transitions. Support your arguments with relevant evidence such as statistics or examples, elaborating on the cause and effect relationships while considering alternative explanations for the effects discussed.
Conclude by summarizing key points and discussing potential implications. Lastly, revise and edit your essay thoroughly for clarity, coherence, and correctness, ensuring that your analysis effectively communicates the connections between events and their consequences. Check out these examples. Struggling with your cause and effect assignment? Don’t worry, expert assistance is just a click away! Reach out to our professionals for the best guidance and ace your assignment with ease.
